Augmented logistics represents a groundbreaking shift in the logistics and supply chain sector, propelled by the integration of augmented reality (AR) and other cutting-edge digital technologies. This innovative approach seeks to enhance traditional logistics operations by overlaying digital information onto the physical world, thereby improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall resilience within the industry. The emergence of augmented logistics is a direct response to the industry’s escalating demand for more sophisticated, agile, and customer-focused solutions. It symbolizes a pivotal step towards addressing complex logistical challenges through technological empowerment.
As we delve into the realm of augmented logistics, this article aims to shed light on its foundational elements, explore the transformative impact of emerging trends and technologies, and discuss the profound implications these advancements hold for the future of the logistics sector. Our objective is to provide a comprehensive overview of how augmented logistics is set to redefine industry standards, streamline operations, and set a new benchmark for excellence in logistics and supply chain management.
The Evolution of Augmented Logistics
From Traditional to Augmented
The journey from traditional logistics practices to the advent of augmented logistics has been marked by significant technological evolution. Traditional logistics, often characterized by manual processes and limited technology use, has gradually embraced digital innovations, paving the way for augmented logistics. This transition underscores a shift from relying solely on physical logistics operations to incorporating digital overlays that enhance real-world interactions.
Technological Catalysts
The transformation towards augmented logistics has been fueled by several key technological advancements. Augmented Reality (AR), with its ability to superimpose digital information onto the physical environment, offers unparalleled opportunities for visualizing complex data and instructions in real-time. The Internet of Things (IoT) extends this capability by connecting devices and sensors across the logistics network, providing a continuous stream of data for monitoring and analysis. Artificial Intelligence (AI) further complements these technologies by analyzing vast amounts of data to derive insights, predict outcomes, and automate decision-making processes. Together, these technologies form the backbone of augmented logistics, enabling more efficient, responsive, and intelligent logistics operations.
Emerging Trends in Augmented Logistics
AR for Enhanced Warehouse Operations
In the realm of warehouses and fulfillment centers, augmented reality is revolutionizing traditional operations. AR applications facilitate inventory management by visually guiding workers to item locations and providing instant access to product information. Training is another area where AR makes a significant impact, offering immersive experiences that accelerate learning and improve retention. Additionally, AR streamlines operational processes by overlaying picking and packing instructions directly onto workers’ field of view, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
IoT and Real-Time Data Integration
The integration of IoT devices throughout the logistics chain has ushered in an era of real-time data availability. Sensors attached to packages, pallets, and vehicles transmit valuable information on location, condition, and environmental factors, enabling logistics operators to track shipments with unprecedented accuracy and respond proactively to any issues. This real-time data integration is crucial for optimizing logistics operations, from route planning to inventory management, ensuring that every decision is informed by the latest information.
AI and Predictive Analytics
AI and predictive analytics are at the forefront of driving strategic decision-making in logistics. By leveraging historical data and current trends, AI algorithms can forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify the most efficient delivery routes. Predictive analytics also plays a vital role in risk management, allowing companies to anticipate potential disruptions and implement contingency plans effectively. The use of AI in logistics not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures a more proactive approach to meeting customer demands and managing the supply chain.
As we explore the future of augmented logistics, it’s clear that the integration of AR, IoT, and AI technologies is not just reshaping the logistics sector but also setting the stage for a more agile, informed, and customer-centric future. The potential of these technologies to transform logistics operations is immense, promising a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in the industry.
How to Implement Augmented Logistics
Implementing augmented logistics involves a strategic approach that incorporates the latest digital technologies to revolutionize logistics operations. Here’s how businesses can embark on this transformative journey:
Starting with AR
Integrating Augmented Reality (AR) into logistics operations begins with identifying areas where AR can significantly impact, such as warehouse operations, training, and maintenance. Start with pilot projects that focus on specific processes or tasks to assess the technology’s effectiveness and gather insights. For instance, implementing AR for picking and packing processes can help determine its efficacy in reducing errors and improving speed. Based on the pilot’s success, companies can gradually scale up AR integration, expanding its application across different areas of logistics operations for comprehensive enhancement.
Building a Technologically Agile Infrastructure
Creating an infrastructure capable of supporting AR, IoT, AI, and other digital technologies is crucial for the successful implementation of augmented logistics. This involves upgrading existing IT systems and networks to handle increased data volumes and ensure seamless connectivity. Investing in cloud computing platforms can offer the scalability and flexibility needed to accommodate these technologies. Additionally, ensuring interoperability between different systems and technologies is essential to facilitate smooth data exchange and integration, enabling a unified and efficient augmented logistics operation.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Cultivating an organizational culture that embraces continuous learning and technological adoption is fundamental to the success of augmented logistics. Encouraging open communication, collaboration, and experimentation can foster an environment where innovation thrives. Providing training and development opportunities for employees to learn about new technologies and their applications in logistics is also crucial. Recognizing and rewarding innovative ideas and solutions can further motivate employees to contribute to the organization’s digital transformation efforts.
Unveiling the Era of Augmented Logistics
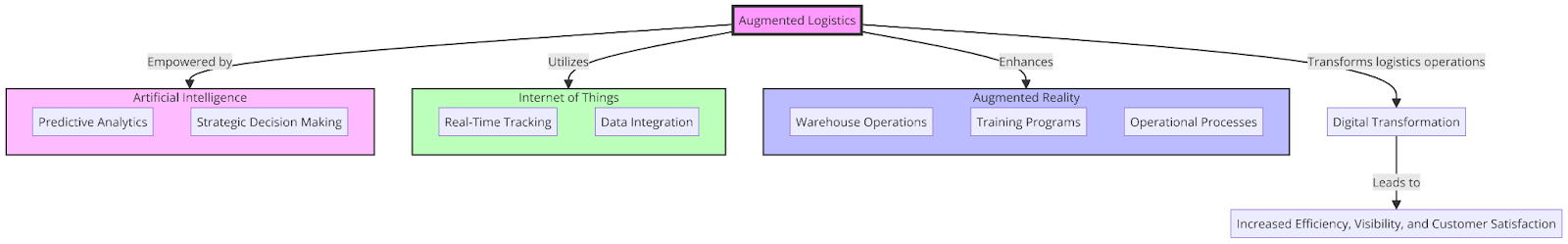
“This diagram visualizes the integration of AR, IoT, and AI in creating augmented logistics, leading to increased efficiency, visibility, and satisfaction.”
Augmented logistics is revolutionizing the logistics and supply chain industry by seamlessly blending digital information with the physical world. This transformative approach is driven by the convergence of augmented reality (AR), the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI), each playing a pivotal role in enhancing traditional logistics operations.
- Augmented Reality (AR) enhances warehouse operations, training programs, and operational processes by overlaying digital information onto the real world, facilitating more efficient, error-free operations.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time tracking and data integration across the logistics network, offering unparalleled visibility and control.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) leverages predictive analytics and strategic decision-making to optimize logistics operations, predict demand, and automate key processes.
This digital transformation is not just about technological adoption but signifies a shift towards more agile, informed, and customer-centric logistics operations. Augmented logistics embodies the future of the industry, promising a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. By embracing these digital advancements, logistics companies can not only streamline their operations but also enhance customer satisfaction and achieve a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving global market.
5 Key Benefits of Augmented Logistics
The implementation of augmented logistics brings a host of advantages that can significantly enhance logistics operations:
1. Operational Efficiency
Augmented logistics streamlines operations and reduces manual errors through the automation of routine tasks and the application of AR for precise execution of complex processes. This leads to faster throughput times, reduced reliance on manual labor, and minimized errors, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
2. Enhanced Visibility and Transparency
The integration of AR and IoT devices provides unparalleled visibility into the supply chain, from real-time tracking of shipments to monitoring the condition of goods in transit. This transparency enables logistics companies to make informed decisions, respond proactively to any issues, and maintain a high level of control over their operations.
3. Improved Safety and Training
AR tools significantly enhance safety and efficiency in employee training programs by providing immersive, interactive learning experiences. Virtual simulations of warehouse operations, for example, allow employees to practice and master tasks in a safe environment, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall workplace safety.
4. Cost Reductions
The long-term cost savings associated with augmented logistics are substantial. By optimizing operations, reducing errors, and improving efficiency, companies can lower operational costs. Additionally, the enhanced accuracy and efficiency in inventory management and order fulfillment processes contribute to reduced waste and better resource utilization.
5. Customer Satisfaction
The impact of augmented logistics on improving delivery times and enhancing customer service is profound. With faster, more reliable delivery services and the ability to provide customers with real-time information about their orders, companies can significantly improve customer satisfaction levels, fostering loyalty and encouraging repeat business.
The future of augmented logistics is bright, offering transformative potential for the logistics sector. By embracing AR, IoT, AI, and fostering a culture of innovation, companies can unlock numerous benefits, including operational efficiency, enhanced visibility, and improved customer satisfaction, positioning themselves for success in the competitive landscape of the digital age.
The Future Directions for Augmented Logistics
The logistics industry stands on the brink of a transformative era, heralded by the integration of augmented reality (AR) and other digital technologies. As we look towards the horizon, the potential applications and challenges of augmented logistics paint a picture of an exciting yet complex future.
Next-Gen AR Applications
The future of AR in logistics promises to extend far beyond its current applications, venturing into realms that could redefine the industry’s operational norms. Next-gen AR applications could enable more sophisticated visualization of logistics networks, allowing for real-time, 3D representations of supply chains. Imagine AR glasses that not only guide warehouse workers to the exact location of items but also display the most efficient path through the warehouse in real-time. Beyond visualization, AR could be pivotal in remote maintenance and repair of logistics infrastructure, where technicians can receive augmented overlays of machinery in need of repair, complete with step-by-step instructions and remote expert assistance.
Integration Challenges and Solutions
Adopting augmented logistics at scale presents a unique set of challenges, chief among them being the integration of AR and digital technologies with existing logistics systems. Compatibility issues, data silos, and the sheer scale of implementation can be daunting. To overcome these challenges, logistics companies must invest in modular, scalable technology platforms that can seamlessly integrate with both legacy systems and cutting-edge technologies. Developing standardized protocols for data exchange and ensuring interoperability across different systems and technologies will be crucial. Additionally, partnerships with technology providers can offer access to expertise and solutions tailored to the specific needs of logistics operations.
Strategic Planning for Future-Ready Logistics
For logistics companies to thrive in the age of augmented logistics, strategic planning and foresight are imperative. This entails not only keeping abreast of technological advancements but also actively engaging in scenario planning to anticipate future trends. Companies must cultivate a culture of innovation, encouraging experimentation and the adoption of new technologies. Investing in employee training and development will be key to building a workforce capable of leveraging augmented logistics technologies. Moreover, a focus on sustainability and resilience will ensure that logistics operations are not only efficient and competitive but also adaptable to the changing global landscape.
FAQs on Augmented Logistics
What exactly is augmented logistics?
Augmented logistics refers to the integration of augmented reality (AR) and other digital technologies into logistics operations to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and visibility. Unlike traditional logistics, which relies heavily on manual processes and physical documentation, augmented logistics uses digital overlays and real-time data to streamline operations and improve decision-making.
How can companies start integrating augmented reality into their logistics operations?
Companies can start by identifying specific areas within their logistics operations where AR can have an immediate impact, such as warehouse picking or training. Implementing pilot projects to test and refine AR applications before a full-scale rollout is advisable. Collaboration with AR technology providers for customized solutions and investing in the necessary hardware and software infrastructure are also critical steps.
What are the main technological requirements for implementing augmented logistics?
Implementing augmented logistics requires a robust IT infrastructure, including high-speed internet connectivity, AR-compatible hardware (such as smart glasses or mobile devices), and access to cloud computing services. Additionally, integrating AR with existing logistics management systems and IoT devices necessitates advanced software platforms capable of processing and analyzing large volumes of real-time data.
Are there any significant challenges or limitations to adopting augmented logistics?
Challenges include the high initial investment in technology and infrastructure, the need for significant cultural and operational shifts within organizations, and potential technical issues related to data integration and interoperability. Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning, investment in training and development, and partnerships with technology providers.
In Conclusion
Augmented logistics represents a pivotal advancement in the logistics sector, propelled by the integration of AR, IoT, AI, and other digital technologies. This evolution promises to enhance operational efficiency, improve safety and training, reduce costs, and significantly boost customer satisfaction. However, realizing the full potential of augmented logistics necessitates overcoming integration challenges and adopting a forward-looking strategic approach. As the logistics industry continues to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the importance of embracing augmented logistics cannot be overstated. It is not merely an option but a strategic imperative for future-proofing the industry, underscoring the critical need for continuous innovation, adaptation, and comprehensive strategic planning to harness the transformative power of augmented logistics in shaping a more efficient, resilient, and customer-centric future.