Logistics is the backbone of any business that deals with the movement of goods and services. This complex field involves the planning, implementation, and control of efficient forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption. The most crucial function of logistics is ensuring that the right products reach the right place at the right time, in the right condition, and at the right cost. This article explores the various critical functions of logistics, their importance, and how they interconnect to drive business success.
Transportation Management
Transportation management is often considered the heart of logistics. It involves the movement of goods from one location to another using various modes of transport, such as road, rail, air, and sea. Efficient transportation management ensures timely delivery of goods, minimizes transportation costs, and enhances customer satisfaction. Key aspects include route optimization, carrier selection, and transportation mode analysis. Advanced transportation management systems (TMS) aid in optimizing routes, tracking shipments in real-time, and managing transportation costs effectively. By selecting the most efficient transportation methods and routes, businesses can significantly reduce costs while ensuring timely deliveries, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Warehousing and Storage
Warehousing and storage play a crucial role in logistics by providing a place to store goods until they are needed. Effective warehouse management involves optimizing the layout for efficient storage and retrieval, managing inventory levels, and ensuring the safe storage of goods. Modern warehouses use technologies like automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and robotics to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Proper warehousing strategies can significantly reduce storage costs and improve order fulfillment times. Efficient warehousing ensures that products are readily available to meet customer demand, reducing lead times and enhancing service levels.
Inventory Management
Inventory management involves overseeing the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and ultimately to customers. It ensures that there is enough stock to meet customer demand without overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. Techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory, economic order quantity (EOQ), and ABC analysis help in maintaining optimal inventory levels. Effective inventory management improves cash flow, reduces holding costs, and ensures product availability, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction. The integration of inventory management systems allows for real-time tracking of stock levels, accurate demand forecasting, and automatic reordering, all of which contribute to a more responsive and efficient supply chain.
Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the process of receiving, processing, and delivering orders to customers. It includes order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Efficient order fulfillment ensures that customers receive the correct products in a timely manner. The use of order management systems (OMS) and integration with e-commerce platforms streamlines the process, reduces errors, and improves delivery times. High order accuracy and timely delivery are critical for maintaining customer trust and loyalty. Advanced order fulfillment strategies, such as automation and the use of robotics, can further enhance efficiency and speed, meeting the high expectations of modern consumers.
Supplier and Vendor Management
Supplier and vendor management is essential for maintaining a reliable supply chain. It involves selecting the right suppliers, negotiating contracts, managing relationships, and evaluating performance. Strong supplier relationships ensure the timely delivery of high-quality materials, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules and meeting customer demands. Effective supplier management reduces risks, improves supply chain resilience, and fosters long-term partnerships. Building strong supplier relationships through regular communication, performance reviews, and collaboration can lead to better terms, consistent quality, and reliable deliveries, all of which are vital for seamless operations.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics refers to the process of returning products from customers back to the manufacturer or retailer. This can include returns, recycling, refurbishing, and disposal of products. Efficient reverse logistics is essential for managing returns cost-effectively, minimizing waste, and ensuring customer satisfaction. It also plays a critical role in sustainability by facilitating the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing the environmental impact of products. Companies with robust reverse logistics processes can recover value from returned products and reduce the costs associated with returns and disposal, contributing to overall profitability.
Technology and Automation
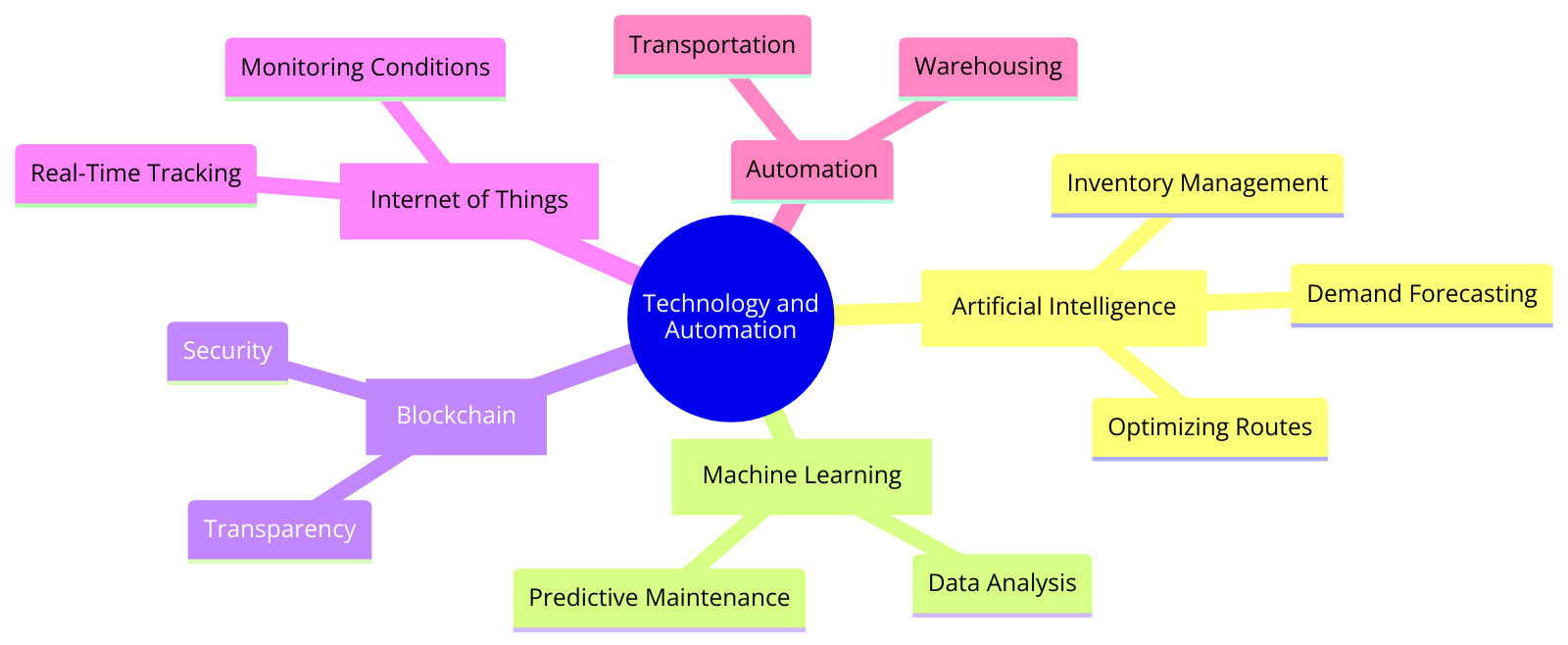
“This mindmap illustrates the key technologies and automation strategies transforming logistics, including AI, machine learning, blockchain, IoT, and their roles in optimizing logistics processes.”
Technology and automation are transforming logistics by improving efficiency, accuracy, and visibility across the supply chain. Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are being integrated into logistics operations. These technologies enhance decision-making, optimize logistics processes, and provide real-time tracking and visibility. Automation in warehousing, transportation, and inventory management reduces human error, speeds up processes, and lowers operational costs. For instance, AI can optimize route planning, forecast demand accurately, and manage inventory levels efficiently, while IoT devices can track shipments in real time and monitor the condition of goods during transit.
In Conclusion
The heart of logistics lies in its ability to coordinate and optimize the flow of goods, information, and finances from origin to consumption. Transportation management, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, supplier management, reverse logistics, and the integration of technology and automation are all crucial functions that interconnect to drive efficiency and customer satisfaction. Understanding and effectively managing these functions are essential for businesses to thrive in today’s competitive market. For further insights and strategies on optimizing your logistics operations, exploring resources from industry experts and staying updated with the latest technological advancements can provide valuable guidance.