In the complex world of logistics and supply chain management, ensuring the safety of workers and the proper handling of hazardous materials is paramount. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are crucial documents that serve this purpose by providing detailed information about the properties, hazards, and safety measures associated with chemical substances. These documents are not only essential for regulatory compliance but also play a vital role in protecting employees, enhancing emergency preparedness, and promoting a culture of safety. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of SDS in logistics, detailing how they protect workers, ensure compliance, and contribute to overall operational safety.
What is a Safety Data Sheet?
A Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is a standardized document that provides comprehensive information about a chemical substance or mixture. Created in accordance with the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), an SDS includes data on the chemical’s properties, health and environmental hazards, protective measures, and safety precautions for handling, storing, and transporting the chemical. Each SDS is structured into 16 sections, making it easier for users to quickly find and understand the necessary information. These sections cover crucial aspects such as identification, hazard identification, composition, first aid measures, firefighting measures, accidental release measures, handling and storage, exposure controls/personal protection, and more. The primary purpose of an SDS is to ensure that workers and emergency responders have access to detailed information that can help them manage and respond to chemical hazards safely and effectively.
The Importance of SDS in Logistics
Safety Data Sheets are indispensable in the logistics sector for several reasons. Firstly, they enhance workplace safety by providing detailed information about the hazards associated with chemicals, thus enabling workers to handle these substances safely. By understanding the risks and necessary precautions, employees can avoid accidents and exposure to harmful chemicals. Secondly, SDS support regulatory compliance. Regulations such as OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard and the EU REACH Regulation mandate the use of SDS for hazardous chemicals, ensuring that businesses adhere to safety standards and avoid penalties. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal issues. Additionally, SDS improve emergency preparedness by providing crucial information that can guide emergency responders during incidents involving chemical spills, leaks, or fires. This ensures that appropriate measures are taken promptly to mitigate the impact of such incidents and protect both workers and the environment.
Key Sections of an SDS
An SDS is divided into 16 sections, each covering specific information about the chemical. Key sections include:
- Identification: Provides the chemical’s name, manufacturer details, and emergency contact information, ensuring that users can quickly identify the substance and seek help if needed.
- Hazard Identification: Describes the chemical’s hazards, including label elements and precautionary statements, helping users understand the risks associated with the substance.
- Composition/Information on Ingredients: Lists the chemical ingredients and their concentrations, providing transparency about the substance’s makeup.
- First Aid Measures: Outlines first aid procedures for various types of exposure, ensuring that appropriate actions can be taken immediately in case of an accident.
- Firefighting Measures: Provides guidelines for fighting fires caused by the chemical, including suitable extinguishing methods and protective equipment.
- Accidental Release Measures: Details procedures for handling spills and leaks, including protective measures to prevent further exposure and environmental contamination.
- Handling and Storage: Offers instructions for safe handling and storage of the chemical, helping to prevent accidents and ensure proper use of the substance.
- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection: Specifies the necessary protective equipment and exposure limits, ensuring that workers are adequately protected from the chemical’s hazards.
How SDS Protect Employees
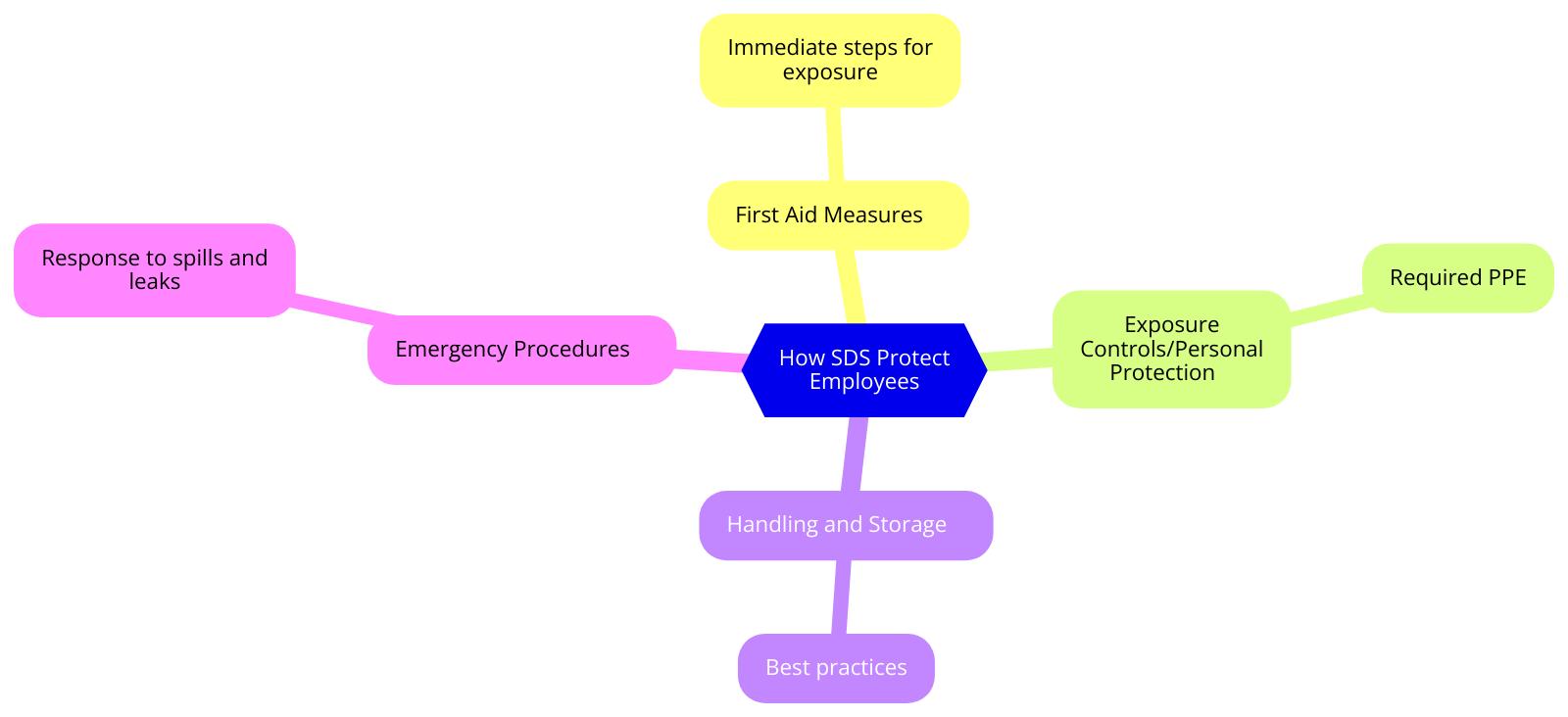
“Illustrating how Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provide essential information for handling hazardous substances safely, ensuring employee protection.”
SDS protect employees by providing the information they need to handle hazardous substances safely. For instance, the “First Aid Measures” section outlines immediate steps to take in case of exposure, while the “Exposure Controls/Personal Protection” section specifies the required personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize risk. By adhering to the guidelines in the SDS, employees can prevent injuries and illnesses related to chemical exposure. The “Handling and Storage” section helps prevent accidents by offering best practices for managing chemicals, ensuring that they are stored and handled in ways that reduce risk. Furthermore, regular training on how to read and understand SDS is crucial. Employers must ensure that all employees are familiar with the information contained in the SDS and know how to use it to protect themselves and others. This training should be part of the initial onboarding process and include regular refreshers to keep safety protocols top of mind.
Regulatory Compliance and SDS
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of managing hazardous substances, and SDS play a central role in meeting these requirements. Agencies like OSHA and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) mandate that SDS be provided for hazardous chemicals. These regulations ensure that employers inform and protect their employees from chemical hazards. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and legal issues. Maintaining up-to-date and accurate SDS is essential for staying compliant with these regulations and avoiding potential fines and sanctions. Regularly reviewing and updating SDS in accordance with regulatory changes is a best practice for maintaining compliance. Additionally, an SDS manager or a designated team should oversee the management of SDS to ensure they are current and accessible to all employees. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also enhances overall workplace safety.
Enhancing Emergency Preparedness
In emergencies involving hazardous substances, quick and informed responses are crucial to minimize harm. SDS provide vital information for emergency responders, including firefighting measures, first aid instructions, and accidental release measures. This information enables responders to take appropriate actions to control the situation effectively. For example, the “Firefighting Measures” section outlines suitable fire extinguishing methods and protective equipment needed, while the “Accidental Release Measures” section provides cleanup procedures and protective measures to prevent further exposure. Having access to detailed SDS ensures that emergency personnel can respond swiftly and safely to chemical incidents. Furthermore, regular drills and training sessions that simulate emergency scenarios can help employees and responders practice the use of SDS, ensuring that everyone knows their role and the procedures to follow in case of an actual emergency.
Training and Accessibility
For SDS to be effective, employees must be trained on how to read and use them. Training programs should cover the interpretation of SDS information, proper handling and storage of chemicals, and emergency response procedures. Additionally, SDS should be readily accessible to all employees at all times. This can be achieved by maintaining physical copies in accessible locations or by using electronic databases that employees can access easily. Ensuring that SDS are available and that employees understand how to use them is critical for maintaining a safe and compliant workplace. Employers should also implement regular refresher courses and updates to ensure that all employees remain informed about any new chemicals or changes in existing safety data sheets. By making SDS training an integral part of the workplace safety culture, companies can enhance their safety protocols and reduce the risk of chemical-related incidents.
In Conclusion
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are vital tools in the logistics industry, providing essential information that protects employees, supports regulatory compliance, and enhances emergency preparedness. By understanding and effectively utilizing SDS, businesses can create safer work environments and ensure that hazardous substances are managed responsibly. Regular training and easy accessibility of SDS are crucial for maximizing their benefits. As regulatory standards evolve, maintaining accurate and up-to-date SDS will remain a cornerstone of effective chemical safety management, helping businesses protect their workforce and operations from the risks associated with hazardous chemicals. In conclusion, investing in proper SDS management and training is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental aspect of fostering a culture of safety and care within the logistics industry.